The Ganges River in India
The Ganges River in India is Sacred to Many
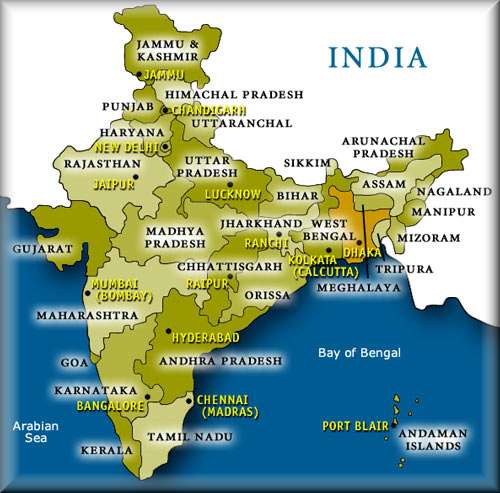
The Ganges River in India is the most famous of India's important river systems and bodies of water. It is the longest river that originates in India, meaning it does not flow into India from another country but instead begins in India and flows elsewhere. The Ganges River actually forms the North Indian River Plain, which is an area that includes most of Northern and Eastern India, parts of Pakistan, Nepal and all of Bangladesh. It also flows east through the Gangetic Region of India, which is located in the North Indian River Plain. The Ganges River in India provides water to approximately forty percent of India's population. It also provides water for irrigation to sustain food crops in India.
Where the Ganges River Begins and Ends
The Ganges River in India begins in the western Himalayan Mountain Range. The Himalayan Mountain Range is located in the Northern Region of India. It is an area with very high altitudes and colder weather than most of India.
The Ganges River then travels from this colder, mountainous Region of India , and it flows eastward through India until it drains into the Sunderbans Delta, which is a waterway located in the Bay of Bengal, in South India.
The average depth of the Ganges River is approximately 52 ft, but it is as deep as 100 ft deep in some areas. The Ganges River Basin drains 39,400 square miles and supplies water to the world's most densely populated country, India. This is one reason that people refer to India as the River of Life. It provides water to many people. Indians that follow the Hindu Religion consider the Ganges River in India to be a holy river.
Many Indian People practice religious rituals and pray at this sacred river every day. Many Indian people also consider the Ganges River to be India's National River. It was actually named after the Hindu Goddess Ganga, due to its life sustaining importance.
Because of the Hindu belief in the god Ganga, and that the Ganges River represents the cycle of life to many Indian People, mourners of the dead often bring their loved ones to the bank of this river. Commonly, funeral ceremonies along the Ganges River involve washing the dead with the water from the Ganges River and then burning the bodies of the dead at its banks.
During these cremation ceremonies, the corpses of the dead are often wrapped in clothe and then burned over mango wood, sandalwood, or other types of wood. In the Hindu religion, it is believed that this ceremony helps take the deceased loved one to their next reincarnated life.
India is mostly surrounded by bodies of water. The Southwestern side of India borders the Arabian Sea, which is part of the Indian Ocean. It has India to the east, Pakistan to the north and Iran on its western side. The surface area of the Arabian Sea is approximately 1,500,000 miles and it gets to be 15,262 ft deep. The Indus River is also really important to India because it was the birthplace of the Indus Vally Civilization, which was the first Indian civilization, and one of mankind's first civilizations.
The Indus River is the largest in Pakistan, and flows directly into the Arabian Sea. Additional rivers in India include the Netravathi, Sharavathi, Narmada, Tapti and Mahi Rivers. Many rivers of the State of Kerala, India also flow into the Arabian Sea. Kerala's coast along central India is called the the Konkan Coast, and its coast along southern India is called the Malabar Coast.
The Indian Ocean is enormous! It's the world's third largest ocean and makes up about twenty percent of Earth's water. It lies directly at India's southernmost tip and is the only ocean that was ever named after a country. To its north is South Asia, on its west side is Africa, east of it is Indochina and Australia, and to its south is the Southern Ocean, near Antarctica. The Indian Ocean is more than 6,000 miles wide from the tips of Africa and Australia, and it covers an enormous area of over 28,000 square miles.
India's lower east side meets with the Bay of Bengal. The Bay of Bengal is considered the most northeastern point of the Indian Ocean. The Bay of Bengal is the largest bay in the entire world and Its borders are defined by Bangladesh to the north, India and Sri Lanka to the west and Andaman and the Nicobar Islands and Burma to the east. These bodies of water and river systems of India make it possible for the country to sustain the world's largest population!
Leave Ganges River and Indian Bodies of Water explore the geography of India.
Find out what it's like in India today!
Discover more of India from our homepage.